DEVELOPMENT OF SPORES AND CHARACTERS OF MYCORRHIZAE
OF THE GENUS SCUTELLOSPORA
In water
|
In PVLG |
||||
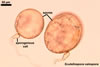
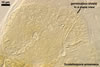
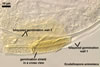
Spores of the genus Scutellospora develop blastically from a bulbous sporogenous cell formed at the end of a fertile hypha connected with mycorrhizal roots (Walker and Sanders 1986). The wall of the most juvenile, expanding spores consists of two, tightly adherent layers of near equal thickness. Then, the inner layer thickens due to addition of new sublayers (laminae). The formation of spore wall ends the differentiation of a third, thin, flexible layer, which usually is tightly adherent to the laminate layer and, hence, difficult to see. Although it was so far revealed only in a few of the Scutellospora species described, e. g. S. armeniaca Blaszk. (Blaszkowski 1992), S. heterogama (Nicol. & Gerd.) C. Walker & F.E. Sanders and S. rubra Stürmer & J.B. Morton (Stürmer and Morton 1999), it probably occurs in spores of all species of the genus. The outermost spore wall layer of Scutellospora spp. is either smooth or ornamented.
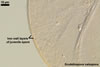
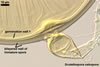
When the differentiation of spore wall layers is completed, two to three separate, bilayered flexible germination walls form. The layers of these walls differ in thickness, plasticity, and reaction to Melzer’s reagent. The ontogeny of spores ends the production of a persistent germination shield associated with the innermost flexible wall.
In PVLG+Melzer's reagent
|
In PVLG
|
||||
In PVLG
|
|||
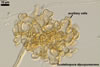
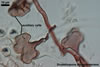
The auxiliary cells produced by Scutellospora spp. are smooth or knobby.
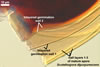
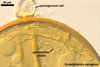
The mycorrhizae of Scutellospora spp. are similar to those of Gigaspora spp., i. e., they consist of only arbuscules and hyphae staining darkly in trypan blue or other stains; no vesicles are produced (Morton 2000). Arbuscules develop from swollen basal hyphae. Intraradical hyphae are straight or coiled and vary in diameter because of the presence of knob-like projections and inflated areas.
REFERENCES
Blaszkowski J. 1992. Scutellospora armeniaca, a new species in Glomales (Zygomycetes) from Poland. Mycologia 84, 939-944.
Morton J. B. 2000. International Culture Collection of Arbuscular and Vesicular-Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi. West Virginia University.
Stürmer S. L., Morton J. B. 1999. Scutellospora rubra, a new arbuscular mycorrhizal species from Brazil. Mycol. Res. 103, 949-954.
Walker C., Sanders F. E. 1986. Taxonomic concepts in the Endogonaceae: III. The separation of Scutellospora gen. nov. from Gigaspora Gerd. & Trappe. Mycotaxon 27, 169-182.